A great way to get started with Stata is using its menus.
The first part of this Tutorial Series introduced you to Stata’s windows. You can now begin learning how to use Stata to work with data.
Across the top are 8 tabs: File, Edit, Data, Graphics, Statistics, User, Window, and Help.
We will not go through every option within the Stata menus. Instead, we’ll highlight a few options to get you started. In this article, we’ll start with three of the most useful menus: File, Data, and Help, along with those helpful icons under the menus.
In our next article, we’ll look at two more: Graphics and Statistics.
(more…)
So, you want to get started with Stata?
Good choice!
At The Analysis Factor we recommend first becoming proficient in one statistical software. Then once you’ve progressed up to learning Stage 3 skills, adding a second statistical software. Whether it’s your first, second, or 5th statistical software, Stata has a lot that makes it worth learning.
When I first started using Stata, I remember being confused by the variety of menus and windows, the strange syntax of the code, the way it handled datasets… and what the heck is a do file? (more…)
Of all the stressors you’ve got right now, accessing your statistical software from home shouldn’t be one of them. (You know, the one on your office computer).
We’ve gotten some updates from some statistical software companies on how they’re making it easier to access the software you have a license to or to extend a free trial while you’re working from home.
(more…)
In a previous post we discussed the difficulties of spotting meaningful information when we work with a large panel data set.
Observing the data collapsed into groups, such as quartiles or deciles, is one approach to tackling this challenging task. We showed how this can be easily done in Stata using just 10 lines of code.
As promised, we will now show you how to graph the collapsed data. (more…)
Panel data provides us with observations over several time periods per subject. In this first of two blog posts, I’ll walk you through the process. (Stick with me here. In Part 2, I’ll show you the graph, I promise.)
The challenge is that some of these data sets are massive. For example, if we’ve collected data on 100,000 individuals over 15 time periods, then that means we have 1.5 million cells of information.
So how can we look through this massive amount of data and observe trends over the time periods that we have tracked? (more…)
Fortunately there are some really, really smart people who use Stata. Yes I know, there are really, really smart people that use SAS and SPSS as well.
But unlike SAS and SPSS users, Stata users benefit from the contributions made by really, really smart people. How so? Is Stata an “open source” software package?
Technically a commercial software package (software you have to pay for) cannot be open source. Based on that definition Stata, SPSS and SAS are not open source. R is open source.
But, because I have a Stata license (once you have it, it never expires) I think of Stata as being open source. This is because Stata allows members of the Stata community to share their expertise.
There are countless commands written by very, very smart non-Stata employees that are available to all Stata users.
Practically all of these commands, which are free, can be downloaded from the SSC (Statistical Software Components) archive. The SSC archive is maintained by the Boston College Department of Economics. The website is: https://ideas.repec.org/s/boc/bocode.html
There are over three thousand commands available for downloading. Below I have highlighted three of the 185 that I have downloaded.
1. coefplot is a command written by Ben Jann of the Institute of Sociology, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland. This command allows you to plot results from estimation commands.
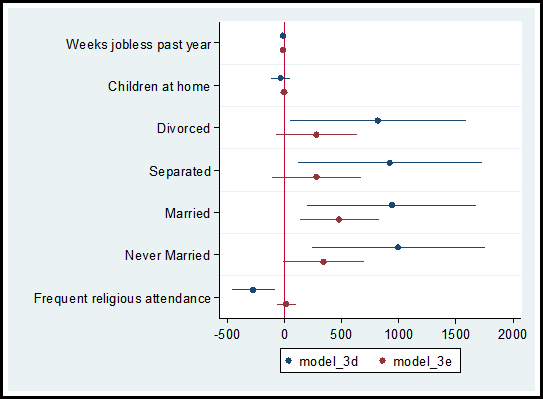
In a recent post on diagnosing missing data, I ran two models comparing the observations that reported income versus the observations that did not report income, models 3d and 3e.
Using the coefplot command I can graphically compare the coefficients and confidence intervals for each independent variable used in the models.
The code and graph are:
coefplot model_3d model_3e, drop(_cons) xline(0)
Including the code xline(0) creates a vertical line at zero which quickly allows me to determine whether a confidence interval spans both positive and negative territory.
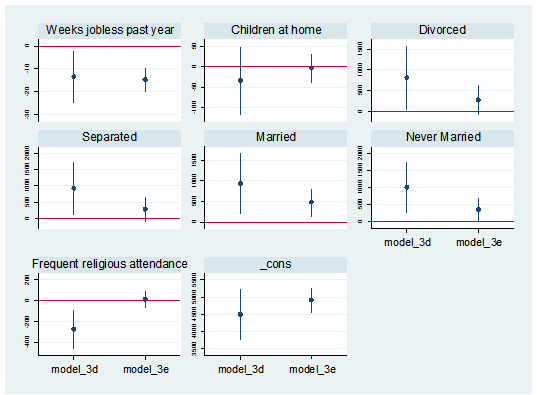
I can also separate the predictor variables into individual graphs:
coefplot model_3d || model_3e, yline(0) bycoefs vertical byopts(yrescale) ylabel(, labsize(vsmall))
2. Nicholas Cox of Durham University and Gary Longton of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center created the command distinct. This command generates a table with the count of distinct observations for each variable in the data set.
When getting to know a data set, it can be helpful to search for potential indicator, categorical and continuous variables. The distinct command along with its min(#) and max(#) options allows an easy search for variables that fit into these categories.
For example, to create a table of all variables with three to seven distinct observations I use the following code:
distinct, min(3) max(7)
In addition, the command generates the scalar r(ndistinct). In the workshop Managing Data and Optimizing Output in Stata, we used this scalar within a loop to create macros for continuous, categorical and indicator variables.
3. In a data set it is not uncommon to have outliers. There are primarily three options for dealing with outliers. We can keep them as they are, winsorize the observations (change their values), or delete them. Note, winsorizing and deleting observations can introduce statistical bias.
If you choose to winsorize your data I suggest you check out the command winsor2. This was created by Lian Yujun of Sun Yat-Sen University, China. This command incorporates coding from the command winsor created by Nicholas Cox and Judson Caskey.
The command creates a new variable, adding a suffix “_w” to the original variable’s name. The default setting changes observations whose values are less than the 1st percentile to the 1 percentile. Values greater than the 99th percentile are changed to equal the 99th percentile. Example:
winsor2 salary (makes changes at the 1st and 99th percentile for the variable “salary”)
The user has the option to change the values to the percentile of their choice.
winsor2 salary, cuts(0.5 99.5) (makes changes at the 0.5st and 99.5th percentile)
To add these three commands to your Stata software execute the following code and click on the links to download the commands:
findit coefplot
findit distinct
findit winsor2
As shown in the December, 2015 free webinar “Stata’s Bountiful Help Resources”, you can also explore all the add-on commands via Stata’s “Help” menu. Go to “Help” => “SJ and User Written Commands” to explore.
Jeff Meyer is a statistical consultant with The Analysis Factor, a stats mentor for Statistically Speaking membership, and a workshop instructor. Read more about Jeff here.




